Surface analysis by x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS)
The surface sensitivity of XPS applied to radioactive materials gives insight into chemical composition of surfaces and interfaces relevant for the safety case study of a nuclear waste repository. Examples are the interaction of dissolved radionuclides with surfaces of corrosion products, colloids of the groundwater, and mineral phases by sorption or incorporation.
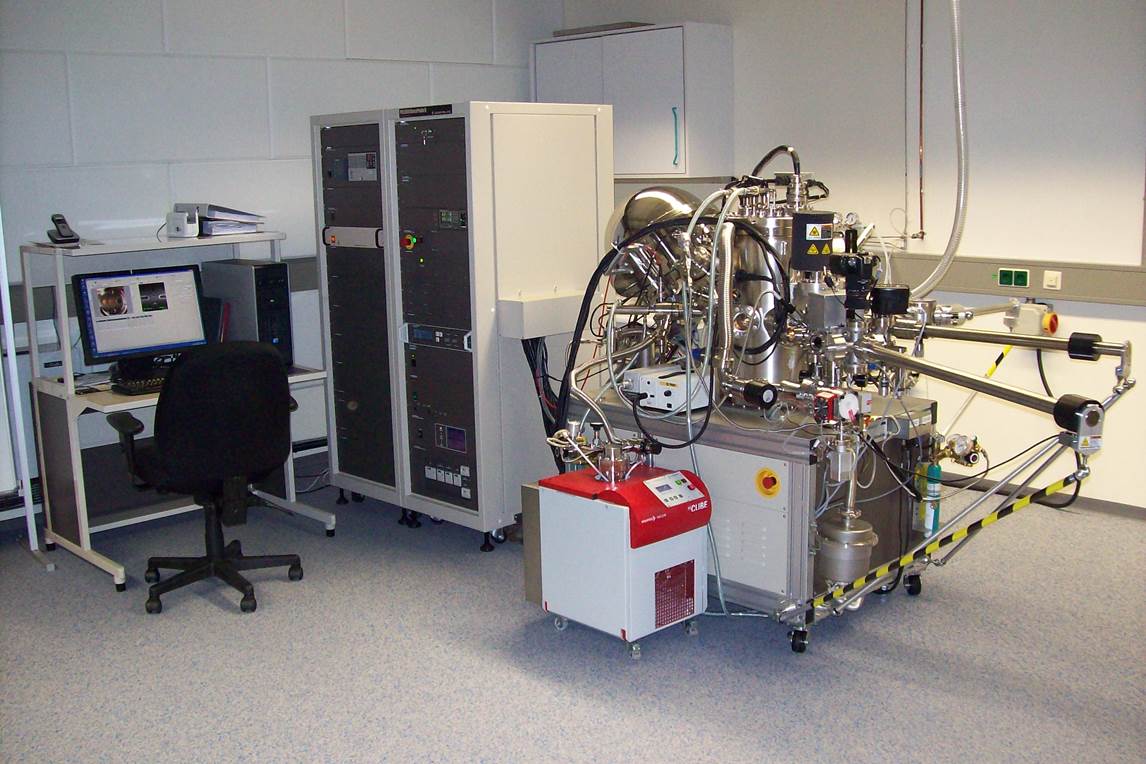
Chemical interaction of a solid material with its environment takes place at its surface, which mostly results in the formation of an interface phase or a layer with a chemical composition differing from that of the bulk. The thickness of such layers may range from monolayers to some nanometers. Knowledge of surface layer properties is essential for understanding of chemical processes occurring at the surface. To identify elements, their valence, and chemical bonding states in the outermost atomic layers of a sample, surface-sensitive x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is applied.
During XPS, the surface of a sample is irradiated by soft x-rays and the photoelectrons leaving the sample are analyzed. The energy of the emitted photoelectrons is essentially given by the difference between x-ray energy and the binding energy of the electrons at their initial atomic energy levels, thus characteristic for each element. By use of the measured photoelectron energies and intensities, the elements and their abundances are identified.
Chemical bonds cause a small shift of the energy of atomic electron levels, measured by high energy resolution XPS as "chemical shift" of the photoelectron energy. Comparison with data from well-known compounds allows drawing conclusion about chemical bonding states at the sample surface.
Contact:
+49 721 608 22521 / 22379
+49 721 608 24602
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
Electron microscopy applied to radioactive materials gives insight into microscopic/ nanoscopic structures relevant for safety assessment of a nuclear repository.
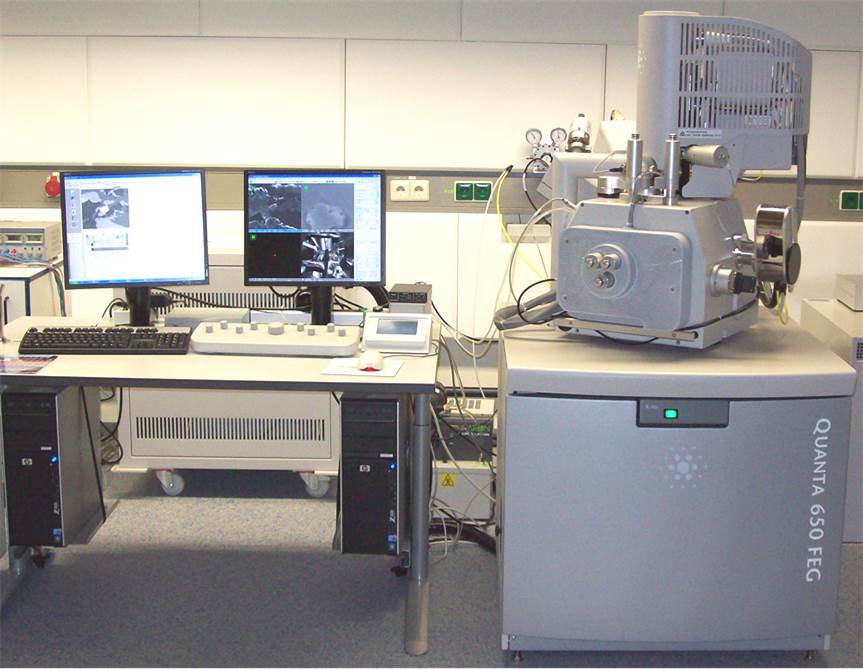
SEM analyses are performed at INE using a FEI QUANTA 650 FEG environmental scanning electron microscope located in the radioactive control area (Fig. 1). In SEM, a fine electron probe is focussed on the surface of a sample and scanned in a two-dimensional raster. At each point, various emitted signals can be detected and contribute to a corresponding point in an image. So-called secondary electrons (SE) enable the observation of surface topography with a lateral resolution down to few nanometers, whereas images produced by means of elastically backscattered electrons (BSE) present an elemental contrast. Furthermore, the detection of characteristic x-rays allows quantitative determination of atomic concentrations at a micrometer scale (energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy, EDX).
Contact:
+49 721 608 22521 / 22379
+49 721 608 24602
Surface analysis by atomic force microscopy (AFM)
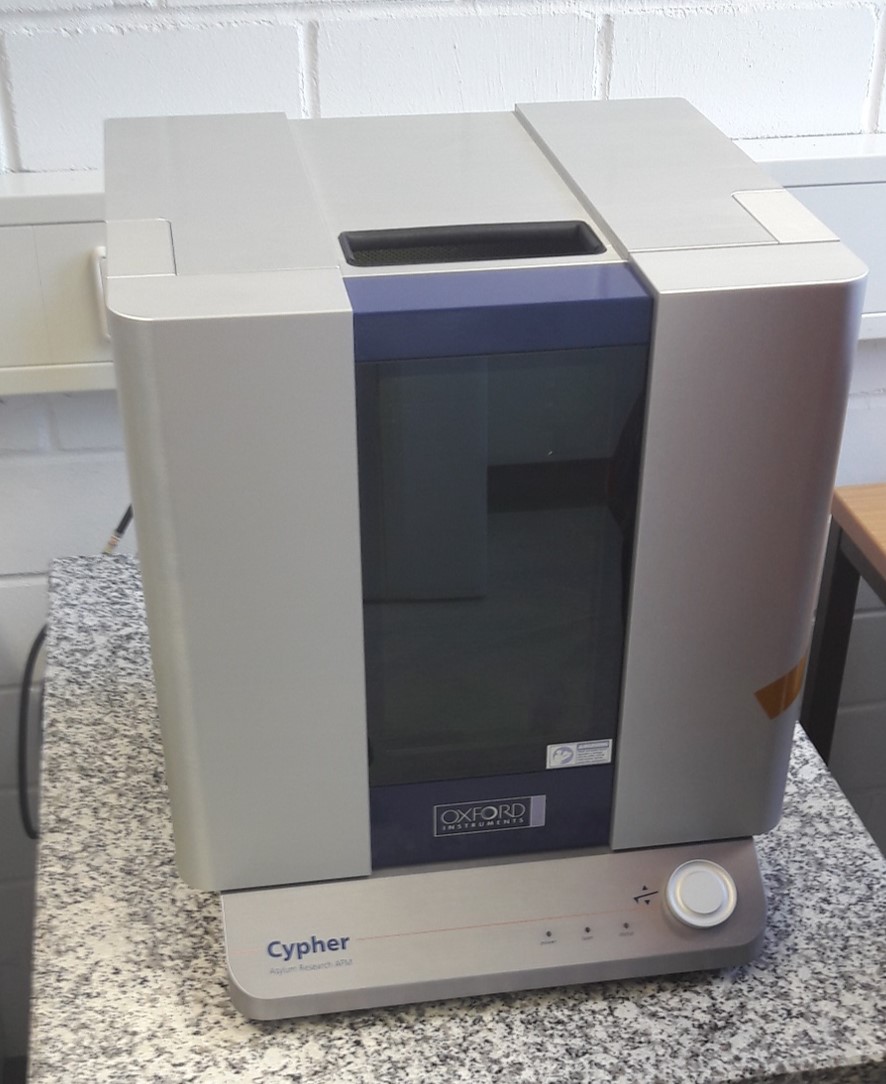
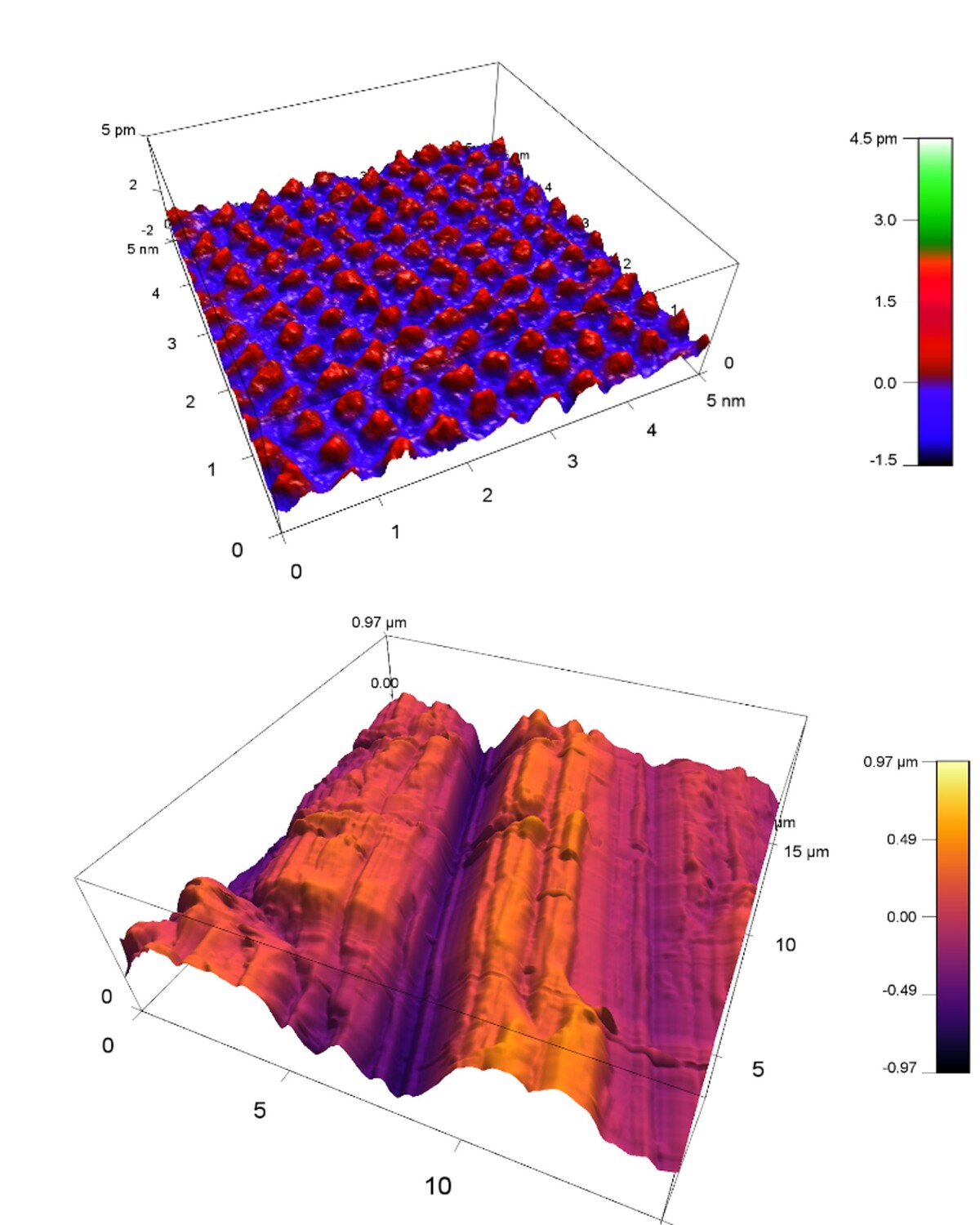
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) allows to measure structures on solid surfaces. In-situ measurements in solution allow monitoring of changes during chemical reactions like crystal growth and dissolution or corrosion. At INE, a Cypher VRS-1250 AFM from Oxford Instruments with various extras like an electro-chemistry cell and the force mapping option is available (Fig. 1). Various measurement modes and scan rates up to video-rate-scanning may be realized. Figure 2 depicts the available range of scales from atomic resolution images of a calcite single crystal surface to relatively large-scale roughness measurements on a polished steel surface.
Contact:
Dr. Frank Heberling +49 721 608 24782
x-ray diffraction
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a non-destructive analytical technique used to identify and to characterize solid samples. Information on the crystallographic structure can be obtained without complex sample preparation and with low amount of sample. For any given crystalline material, both the position and the intensity of the reflections on the diffractogram are indicative of a particular phase (“fingerprint”). Quantitative information on a sample can be obtained from whole powder pattern decomposition, for example by the Rietveld method.
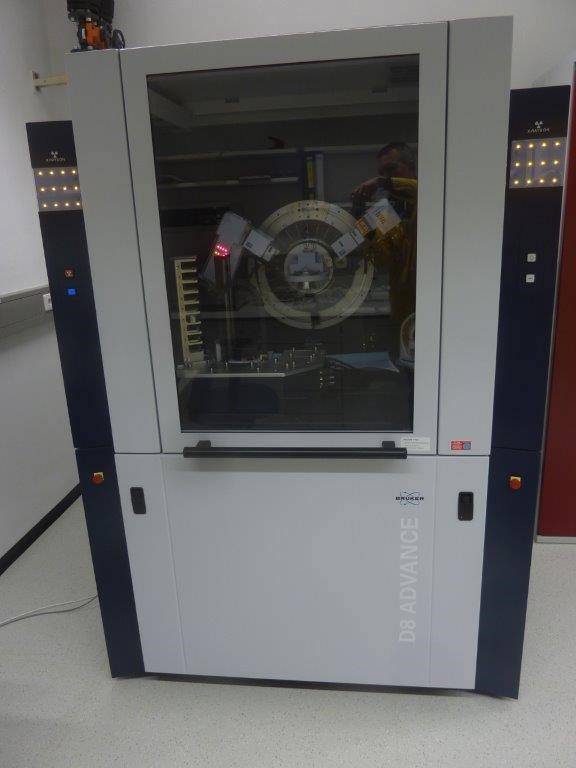
X-ray powder diffractograms are recorded in reflection mode using a D8 Advance A25 diffractometer (Bruker AXS) in Bragg-Brentano geometry (θ - θ) located in the controlled area of INE. X-rays are produced from a Cu anode and the intensity of the scattered radiation is detected with an energy dispersive detector (LynxEye XE-T). Powders, oriented or textured samples (such as sheet silicates), air-sensitive and/or radioactive samples (use of closed and airtight sample holder) can be analyzed using dedicated holders.
Information provided by XRD is of key importance in various areas of research activities at INE. Besides determining the mineralogical composition of natural samples, XRD is used to characterize samples after corrosion experiments (steel, cement waste form…), the purity of synthetic samples from (co)precipitation experiments (retention of radionuclides in solid phases, identification of precipitates).
Contact:
+49 721 608 24321