Development of X-ray Spectroscopies and Radiochemical Applications
Objectives |
|
|
We are developing X-ray spectroscopies to address various questions in radiochemistry and the fields of intermediate nuclear waste storage and disposal research. For example, we (1) conduct geochemical investigations to gain an in-depth understanding of radionuclide migration mechanisms, (2) explore radionuclides and develop generators for radiopharmaceutical applications, and (3) study the mechanisms of lanthanide and actinide toxicology in mammalian cells. |
|
Current Research Topics |
|
|
Fundamental studies:
Applied studies:
|
|
Instruments |
|
|
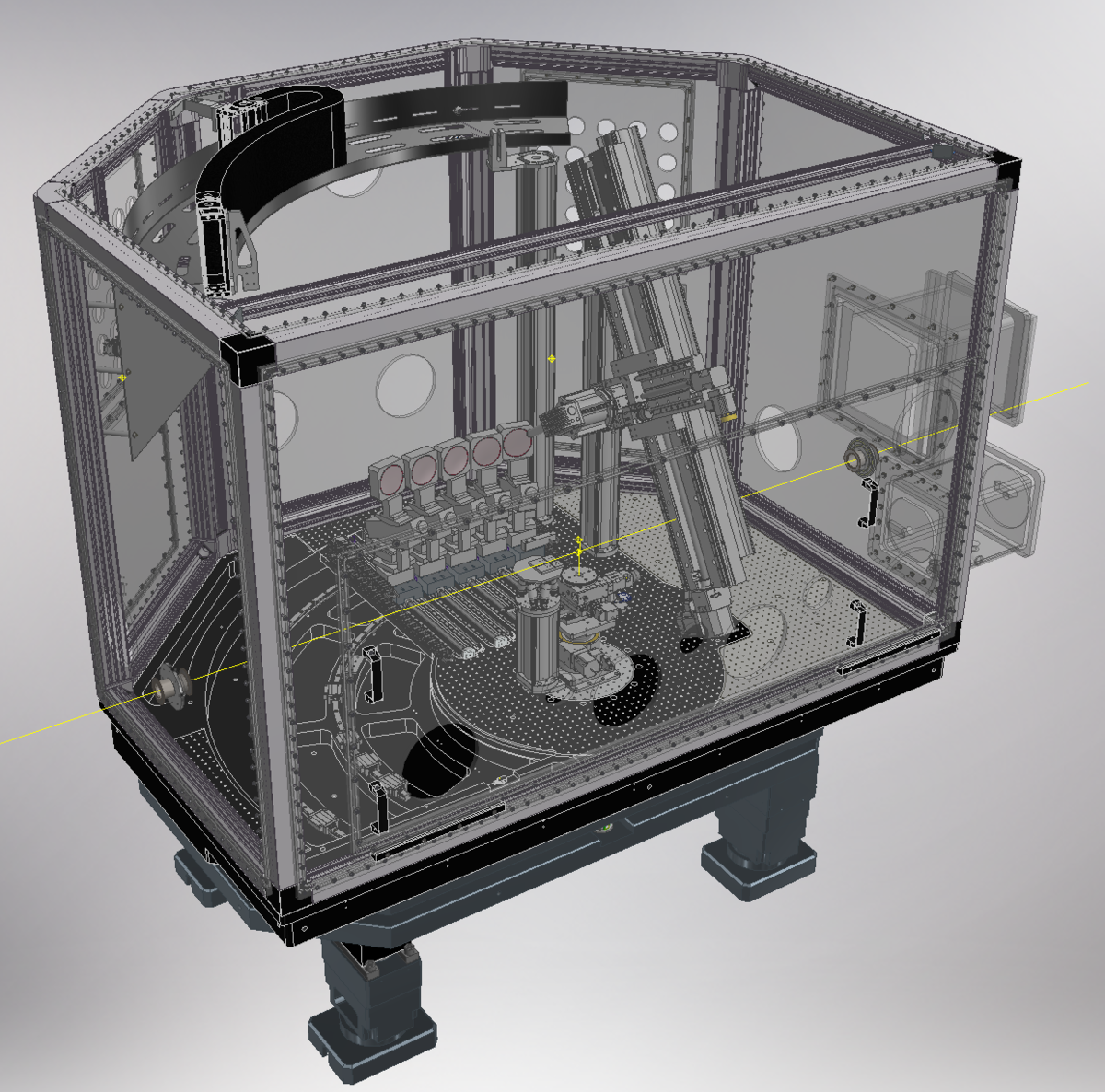
Our studies utilize high-energy resolution X-ray absorption near-edge structure (HR-XANES), X-ray emission spectroscopy (XES), and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) techniques to study the structural properties of actinide (An) elements. The latest upgrade to our NEXT-generation multi-analyzer Johann-type X-ray emission spectrometer (NEXT spectrometer, see the Fig.1) features a rotational table, enabling experiments at 1 m, 0.5 m, 90°, and in backscattering geometry. This is the central instrument at the ACT station for actinide research at the CAT-ACT beamline of the KIT Light Source in Karlsruhe, Germany.
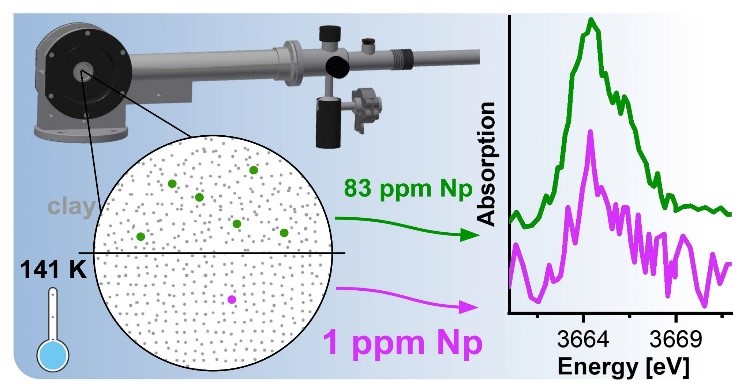
Our setup is optimized for An M4,5-edge HR-XANES and XES/RIXS experiments; absorption of 3–4 keV photons by air is minimized by a helium environment enclosing the sample, crystals, and detector, thereby enhancing efficiency. This instrument, combined with access to the controlled area laboratory at INE in close proximity, is globally unique, enabling An M4,5-edge HR-XANES and XES/RIXS investigations of solid and liquid-phase radioactive materials, including those under extreme conditions. For example, in situ/in operando spectroscopy of solid and liquid actinide compounds can be performed. |
|
Latest Developments |
|
|